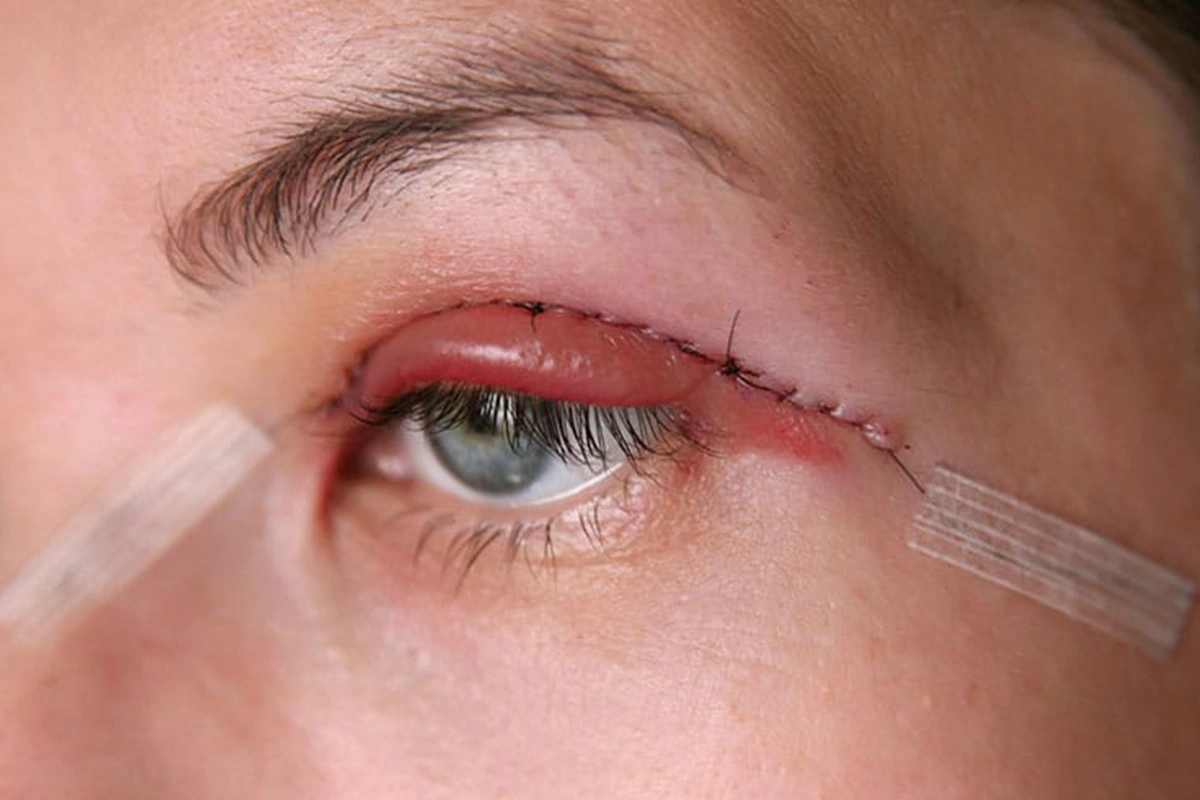
Dr. Joel Kopelman of Kopelman Aesthetic Surgery performs blepharoplasty with levator advancement to lift eyelids and tighten the levator muscle, correcting droopy eyelids and improving both function and appearance.
This combined ptosis surgery treats upper eyelid ptosis, excess skin, and many complex cases of ptosis while also enhancing the patient’s visual field.
Key Takeaways
- Levator advancement surgery removes excess skin and strengthens the levator muscle to improve vision and appearance.
- Average eyelid elevation is 2 to 4 millimeters, measured by margin reflex distance, with more than 90 percent of patients achieving stable results.
- Dr. Kopelman, a board-certified facial plastic and eye surgeon, offers safe and effective surgical approaches tailored to each patient.
- Most swelling resolves in about 10 days, and eyelid height is usually stable within six to eight weeks.
- Options such as Muller’s muscle resection, frontalis suspension, and white-line advancement help in mild or complex cases of ptosis.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Levator Advancement
What Is Levator Advancement?
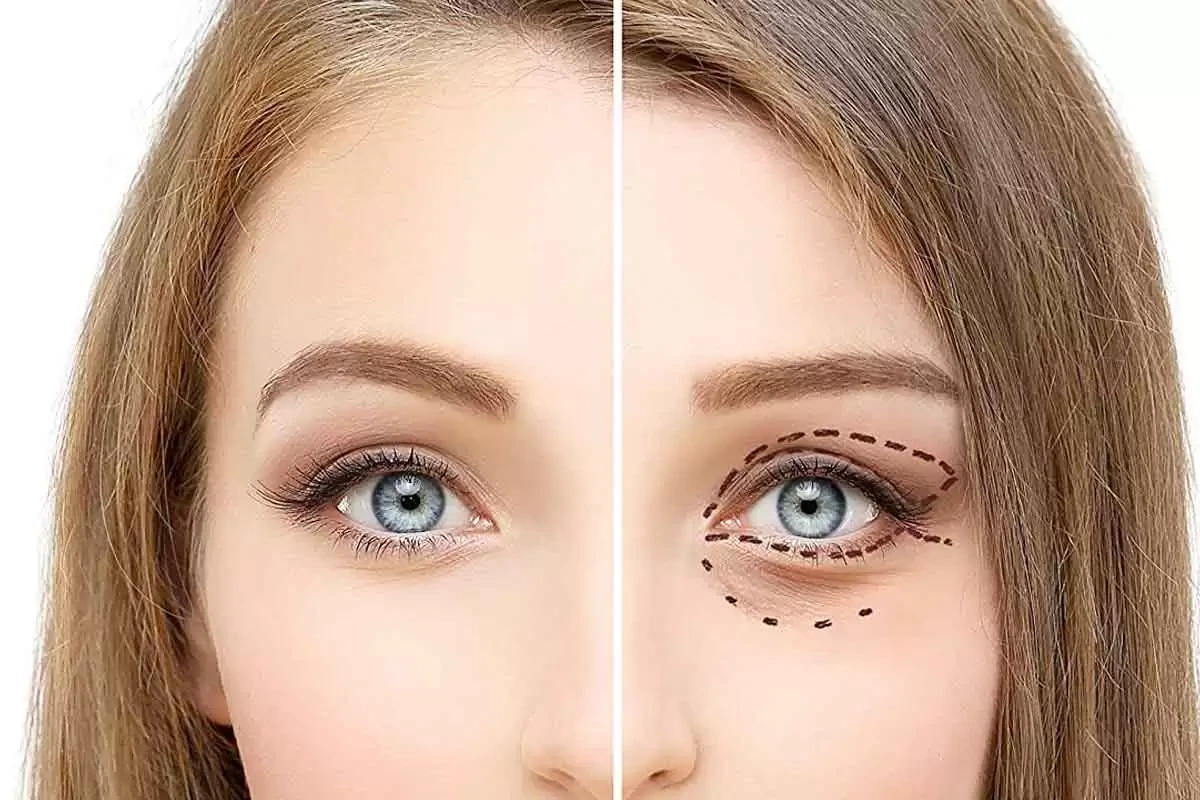
This procedure strengthens the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid. The surgeon shortens or reattaches it to raise the lid while removing excess skin or fat.
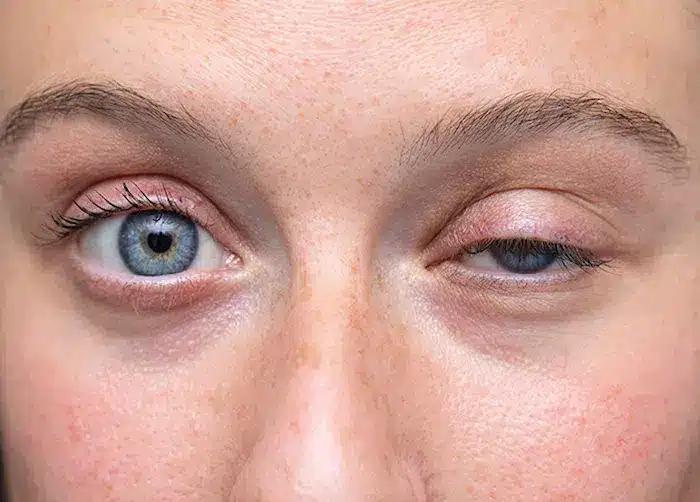
Levator advancement surgery is commonly used in cases of ptosis, including mild ptosis, where weak muscles cause drooping and reduce the visual field. For a clear visual of this anatomy, see this helpful eyelid diagram
Candidate Criteria
Good candidates have droopy eyelids that reduce vision or cause a tired look. A full eye exam and review of health help Dr. Kopelman plan treatment. Patients with mild ptosis benefit when early droop starts to affect reading, driving, or everyday tasks.
Surgical Options and Techniques
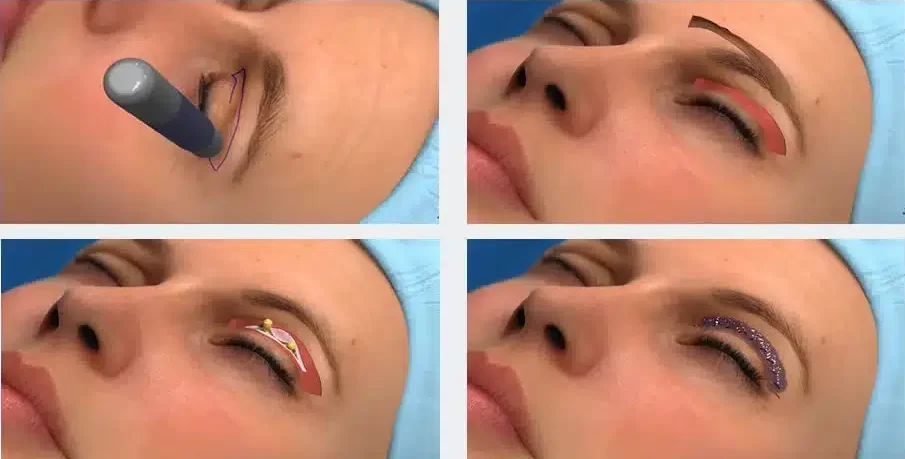
Levator Advancement Steps
Under local anesthesia, a small crease incision is made. The levator muscle is tightened and stitched to improve lid height. The surgeon evaluates the upper lid margin and upper eyelid margins to ensure symmetry and checks the levator aponeurosis for stretching or weakness.
Measurements of margin reflex distance guide the amount of lift needed for proper correction and improved visual field.
External Approaches
Levator advancement and ptosis repair with levator resection are common external approaches performed through a natural eyelid crease. Levator resection removes a segment of the muscle for extra lift, while blepharoplasty removes excess skin or fat.
Clinical Outcomes
Research shows average lid elevation of 2 to 4 millimeters and low complication rates, typically under 5 percent. These surgical approaches give precise correction for upper eyelid ptosis and stable long-term results while expanding the patient’s visual field.
Results and Recovery
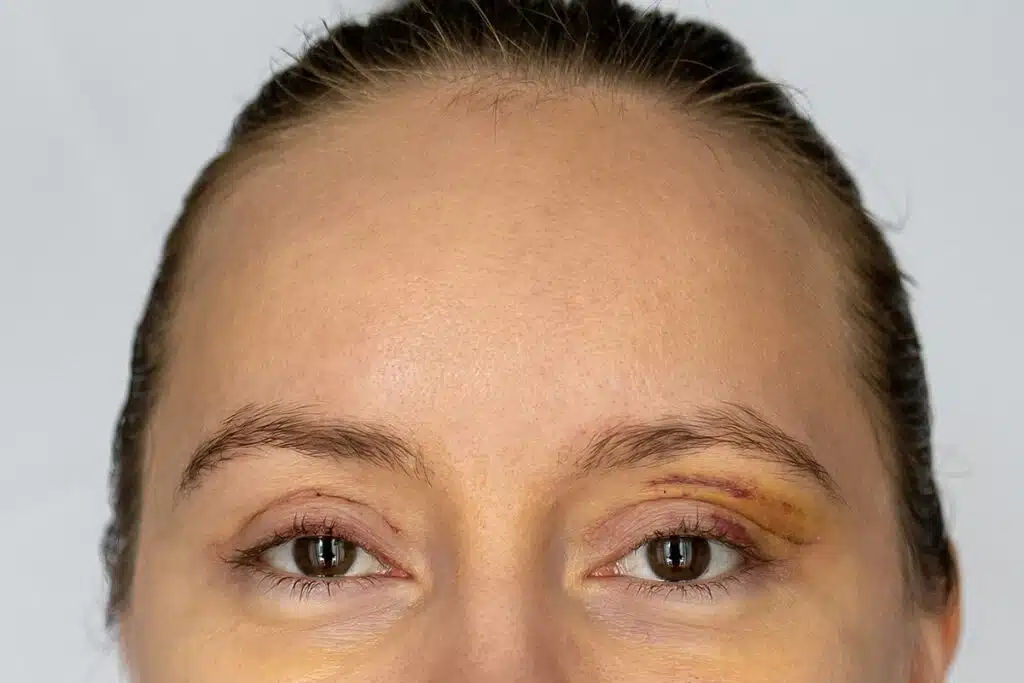
Healing Timeline
Most patients return to normal activities in 7 to 10 days. About 80 percent of swelling resolves within the first 10 days, and near-final height is reached within six to eight weeks. Learn more about the typical recovery process in this detailed guide to blepharoplasty recovery
Long-Term Results
When the levator muscle heals securely, the results last for many years, improving eye appearance and peripheral visual field.
Example Patient
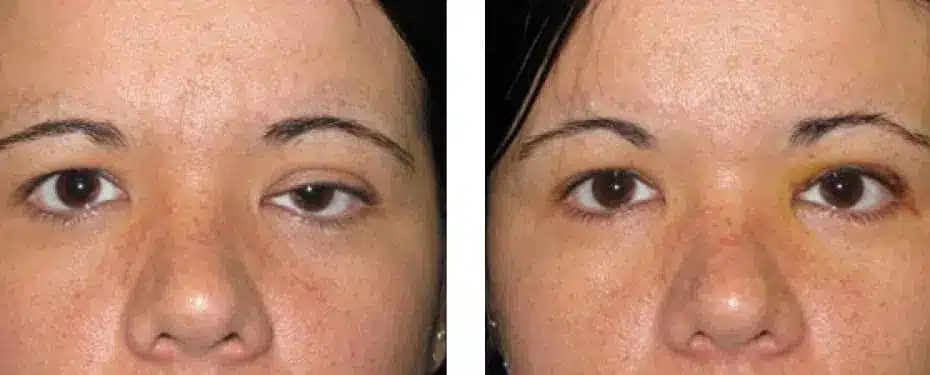
A 62-year-old woman with heavy droopy eyelids underwent levator advancement surgery with blepharoplasty to remove excess skin and strengthen the levator muscle.
After three months, her eyelid height improved by 3 millimeters, her margin reflex distance increased, her visual field widened, and her confidence returned.
Cost and Alternatives
Cost and Insurance
The typical range for levator advancement surgery or combined ptosis repair is $8,500 to $10,000 per eye, which includes surgeon’s fees, facility costs, and anesthesia. Insurance may cover part of the cost if the ptosis surgery improves vision or documented a loss of visual field.
Alternative Procedures
- Muller’s Muscle Resection – For mild ptosis when the levator muscle works well.
- Frontalis Suspension – Uses the frontalis muscle in the forehead for severe droop.
- White-Line Advancement – Advances connective tissue of the levator for precise lift.
Dr. Joel Kopelman combines over 35 years of surgical experience with natural results. A consultation at Kopelman Aesthetic Surgery helps determine whether blepharoplasty with levator advancement, levator advancement surgery, another surgical approach, or a different ptosis repair is best for your needs.
Schedule a consultation today to discuss your goals and receive a personalized treatment plan from Dr. Kopelman.