Calcium filler is a type of dermal filler used to restore structure and support in areas of the face affected by volume loss. It is made with calcium hydroxylapatite CaHA, a mineral-based substance that provides immediate contour and also supports collagen stimulation over time.
This article explains how calcium injectable fillers work, where they are used, and what to know about safety, longevity, and clinical decision-making. The information reflects standard medical guidance used in practices such as Kopelman Aesthetic Surgery, where Dr. Joel Kopelman applies facial plastic and oculoplastic principles to injectable care.
Key Takeaways
- Calcium fillers are a type of dermal filler that provides firm support and stimulates collagen production over time.
- Safety depends on reviewing medical history, using proper injection technique, and choosing the right patient.
- These fillers work best in deeper areas like the cheeks, jawline, neck, and hands, not fine surface lines or facial wrinkles.
- Results appear in stages and often last about 12 months or longer for many patients.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are Calcium Fillers and How Do They Work?
Calcium fillers are injectable treatments used to support areas that lose structure with age. They are different from soft gel fillers because they contain a mineral component. This makes them useful when firmness and shape are needed.
Doctors classify calcium fillers as biostimulatory fillers. They provide early support and encourage collagen stimulation and production over time. This helps maintain structure after the filler gel fades.
How Clinicians Decide When to Use Calcium Fillers
Selecting a filler involves more than choosing a product. Clinicians assess facial structure, tissue depth, and movement patterns before deciding on treatment. Calcium fillers are usually preferred when firm support is needed rather than surface smoothing.
The injection technique plays a key role in this decision. Depth, angle, and placement affect both safety and results. This process explains why calcium fillers are used selectively and not for every aesthetic concern.
What is a calcium hydroxylapatite filler?
A calcium hydroxylapatite filler contains tiny calcium particles mixed in a gel. Calcium hydroxylapatite CaHA is already found in the human body. This supports its compatibility with skin and tissue.
After injection, the gel adds early volume. Over time, the gel absorbs, but the particles stay. They form a support structure in the tissue.
How CaHA fillers stimulate collagen
CaHA fillers activate fibroblasts in the skin. These cells are responsible for collagen production, which helps keep skin firm and supported. This process contributes to long-term collagen development.
Both collagen and elastin help keep skin firm and flexible. Studies have shown significant increases in collagen levels after treatment. This process takes months, not days.
Is Calcium Filler Safe?
Calcium filler is considered safe when it is used correctly by a trained medical professional. Safety depends on proper patient selection, careful injection technique, and a strong understanding of facial anatomy. Like any dermal filler, it carries risks, but serious complications are uncommon when medical guidelines are followed.
Before treatment, clinicians review the patient’s medical history. They also explain risks, benefits, and limits as part of informed consent. This step helps patients make educated decisions.
Who Should and Should Not Get Calcium Fillers
Calcium fillers are not appropriate for every patient. Proper selection helps reduce risks and supports better outcomes. Clinicians evaluate skin thickness, facial anatomy, and treatment goals before recommending this option.
Certain conditions may limit suitability. Patients with very thin skin, active skin infections, or specific autoimmune conditions may require a different approach. A detailed review of medical history helps identify these concerns early and supports safe planning.
Common safety topics include:
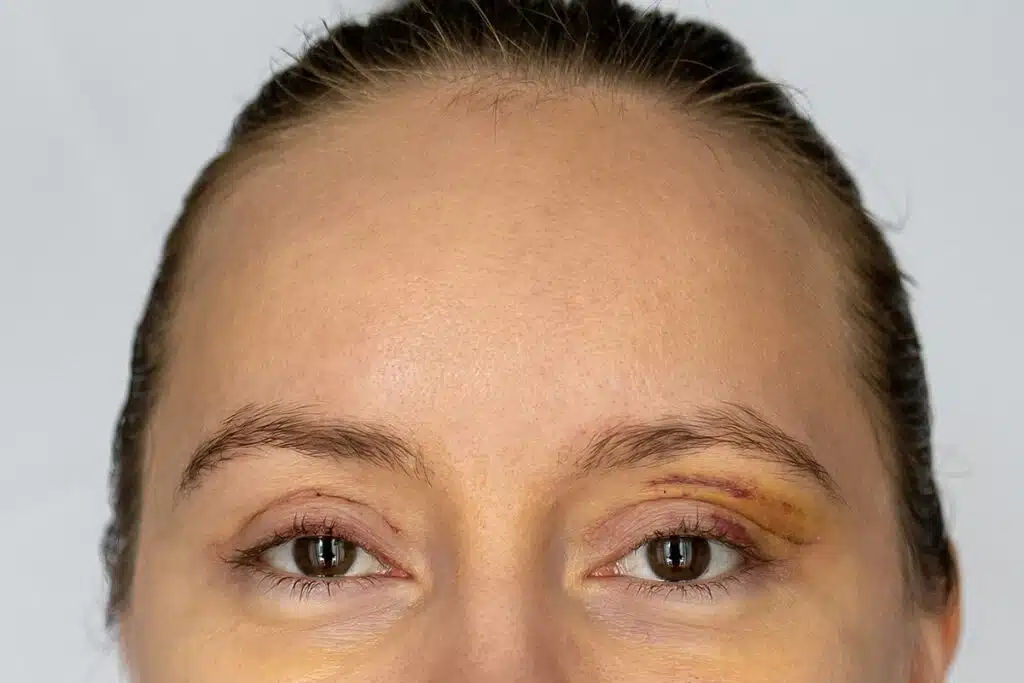
- Temporary swelling, redness, or bruising
- Rare risks from poor placement
- The importance of injector experience
Calcium hydroxylapatite filler side effects
Most side effects are mild and short-lived. These may include swelling, bruising, or soreness at the injection site. They usually improve within a few days.
Serious problems are rare when proper technique is used. Poor injection technique increases risk. Dr. Kopelman has noted in clinical discussions that experience is key to safety.
FDA approval and clinical safety
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approves calcium hydroxylapatite fillers for specific uses. Approval means the product meets safety and performance standards. Manufacturing quality is also monitored.
Clinical studies show predictable behavior when fillers are placed correctly. Compared with other biostimulatory fillers, such as poly-L-lactic acid, calcium fillers have different safety profiles depending on firmness and depth. Medical responsibility always stays with the treating clinician.
Calcium Filler Treatment Areas
Calcium fillers are used in areas that need strong support. They are not suitable for every part of the face. Doctors plan treatment based on anatomy and tissue depth.
These fillers are placed deeper than many other injectables. This helps avoid surface problems and fits their structure.
Calcium filler for face volume and wrinkles
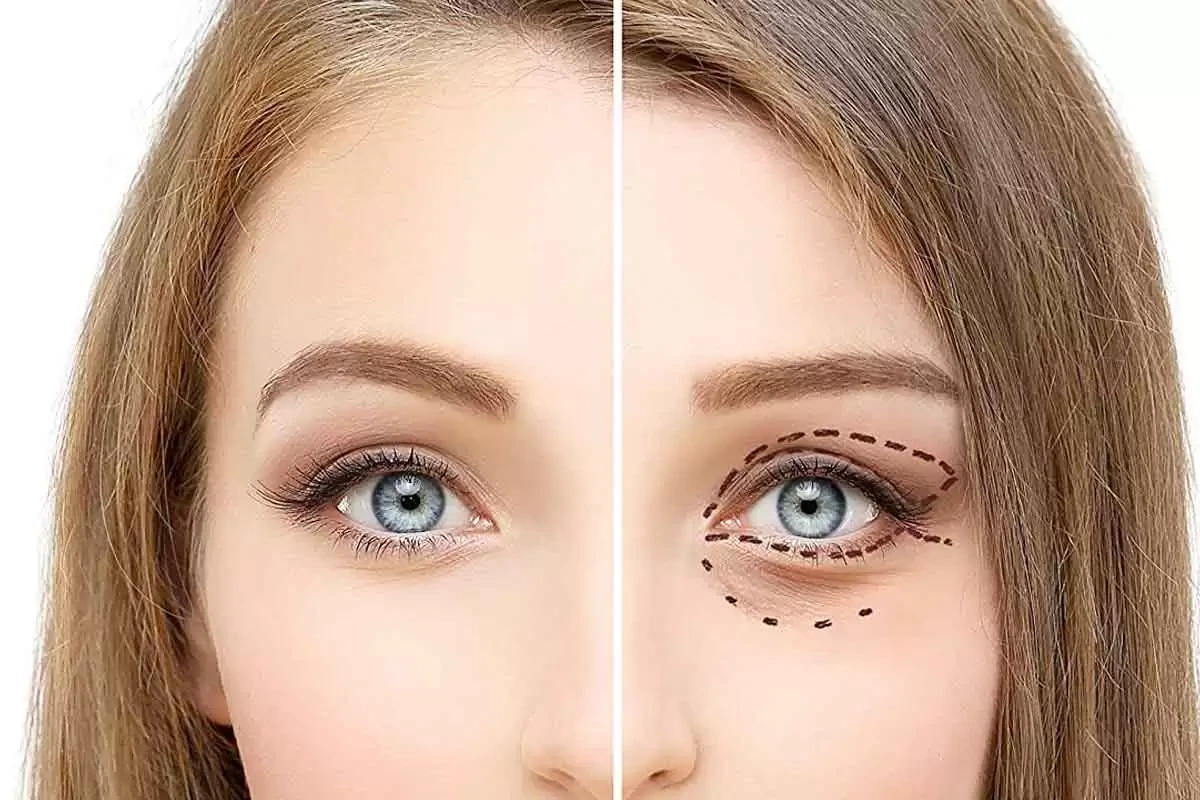
In the face, calcium filler is used for deeper facial wrinkles and volume loss. Common areas include the cheeks, jawline, and nasolabial folds. The goal is to restore structure, not smooth fine lines.
Calcium filler for neck and hands
The neck and hands often show aging due to thin skin and volume loss. Calcium fillers can improve contour and enhance skin appearance when used carefully. The technique is adjusted to protect sensitive areas.
Proper depth is essential to avoid uneven texture. These areas require skill and experience.
Calcium Filler Brands and Clinical Use
Several calcium-based filler products are available. Each has different handling features. Knowing these differences helps guide treatment. Calcium fillers are one option among the most popular fillers, with selection guided by anatomy, treatment goals, and tissue depth.
Calcium filler Radiesse
Radiesse is the most well-known calcium hydroxylapatite filler. It is approved for several aesthetic uses. It provides firm support and allows precise placement.
Radiesse is often chosen for areas that need definition. Correct technique helps achieve predictable results. Its use in delicate areas, such as discussions around Radiesse under the eyes, requires careful anatomical assessment and conservative planning.
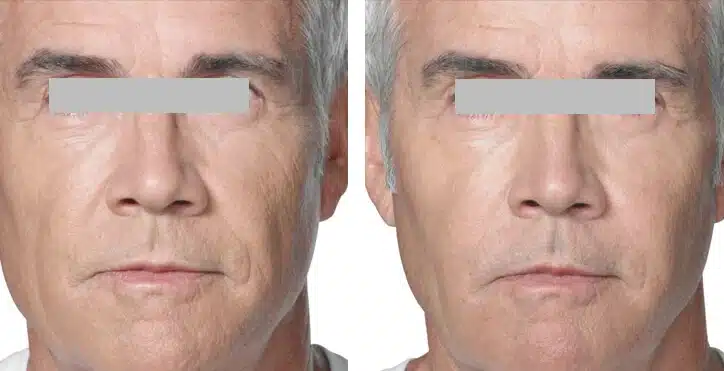
Calcium Fillers Before and After Results
Calcium fillers do not cause sudden changes. Results develop over time. Early changes are driven by the gel, followed by collagen support.
These fillers are not right for every concern. Their firmness makes them less suitable for very superficial or highly mobile areas.
Recovery After Calcium Filler Treatment
Recovery after calcium filler treatment is usually brief. Mild swelling, redness, or tenderness can occur for a few days. Most patients return to normal daily activities shortly after treatment.
Aftercare guidance may include avoiding pressure on the treated area and delaying strenuous exercise. Follow-up visits allow clinicians to assess healing and early results. These steps support patient safety and confidence during recovery.
What results are expected
Many patients see early improvement in shape and support. Over time, collagen stimulation and collagen production help maintain these changes. The goal is a balanced and natural look.
When results become visible
Some changes appear soon after treatment. Others develop over weeks or months. Swelling may briefly affect how results look.
Between 2 and 4 weeks, swelling resolves and the treated area begins to look more natural. From 4 to 8 weeks, collagen production increases, providing firmer support beneath the skin. By 8 weeks, most patients see their stable, long-term result, with gradual refinement continuing beyond that point.
How Long Does Calcium Filler Last?
Longevity of calcium hydroxylapatite fillers
Results often last around 12 months to 18 months. In some cases, long-term collagen support extends the effect. The filler breaks down slowly.
Factors that affect duration
Metabolism, skin quality, and lifestyle matter. Areas with less movement often last longer. Maintenance plans vary.
Calcium Hydroxylapatite Filler vs Hyaluronic Acid
Calcium fillers and hyaluronic acid fillers serve different roles. The choice depends on anatomy and goals. Neither is best for everyone. Calcium hydroxylapatite filler provides firm structural support and works best in deeper tissue. It also signals collagen production over time and is not reversible. Understanding the difference between filler and hyaluronic acid helps patients better evaluate safety, reversibility, and expected results.
Hyaluronic acid filler adds soft, flexible volume in more superficial areas. It attracts water, smooths fine facial wrinkles, and can be dissolved if needed. This comparison helps explain why calcium fillers and hyaluronic acid fillers are often discussed among the best facial fillers for different treatment needs.
Can You Put Filler on Top of Filler?
Layering fillers depends on what was used before and where. Safety guides these decisions. Careful review is needed.
Layering CaHA fillers safely
Doctors must confirm the existing filler type. Poor planning can cause uneven texture. Conservative treatment lowers risk.
Combining calcium and hyaluronic fillers
Calcium and hyaluronic fillers can be used together, but they are placed in different tissue layers. Calcium filler is used first to add deep structural support. Hyaluronic acid filler is then placed closer to the skin to smooth surface lines or refine shape.
How Much Do Calcium Hydroxylapatite Fillers Cost?
Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers typically cost $700 to $1,100 per syringe. The final price depends on the amount of product needed and the treatment area. Some patients may require more than one syringe for adequate support.
What affects pricing
Treatment area, filler amount, and injector experience affect cost. Location also matters. Medical-grade products follow regulations. Broader pricing factors are often discussed when reviewing the overall injectable fillers cost.
Why costs vary by provider
Providers with advanced training may charge more due to expertise and risk control. Dr. Kopelman’s background as a facial plastic and oculoplastic surgeon reflects this level of training. Cost decisions should focus on proper care, not price alone.
If you would like to learn whether calcium filler is appropriate for your concerns, you can schedule a consultation with a qualified specialist. A one-on-one visit allows you to review your goals, anatomy, and medical history, so you can make an informed decision with personalized medical guidance.