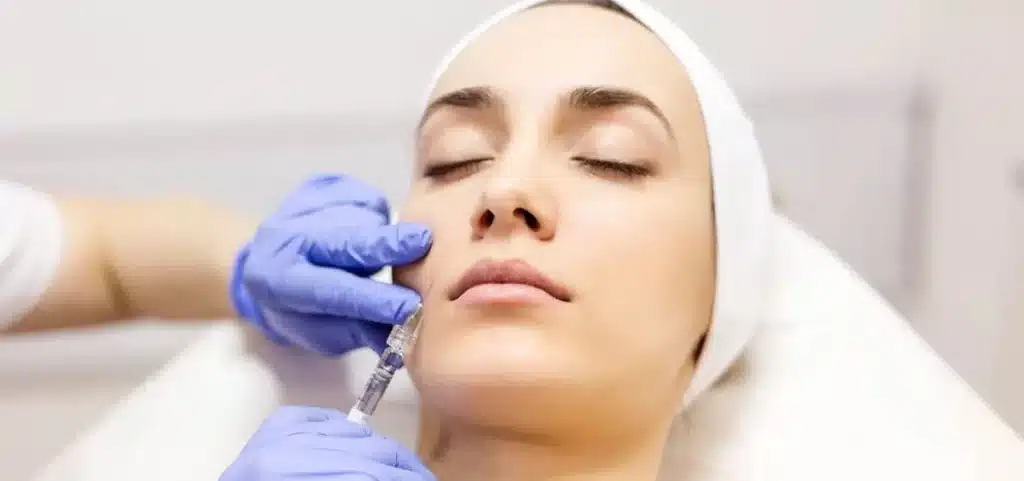
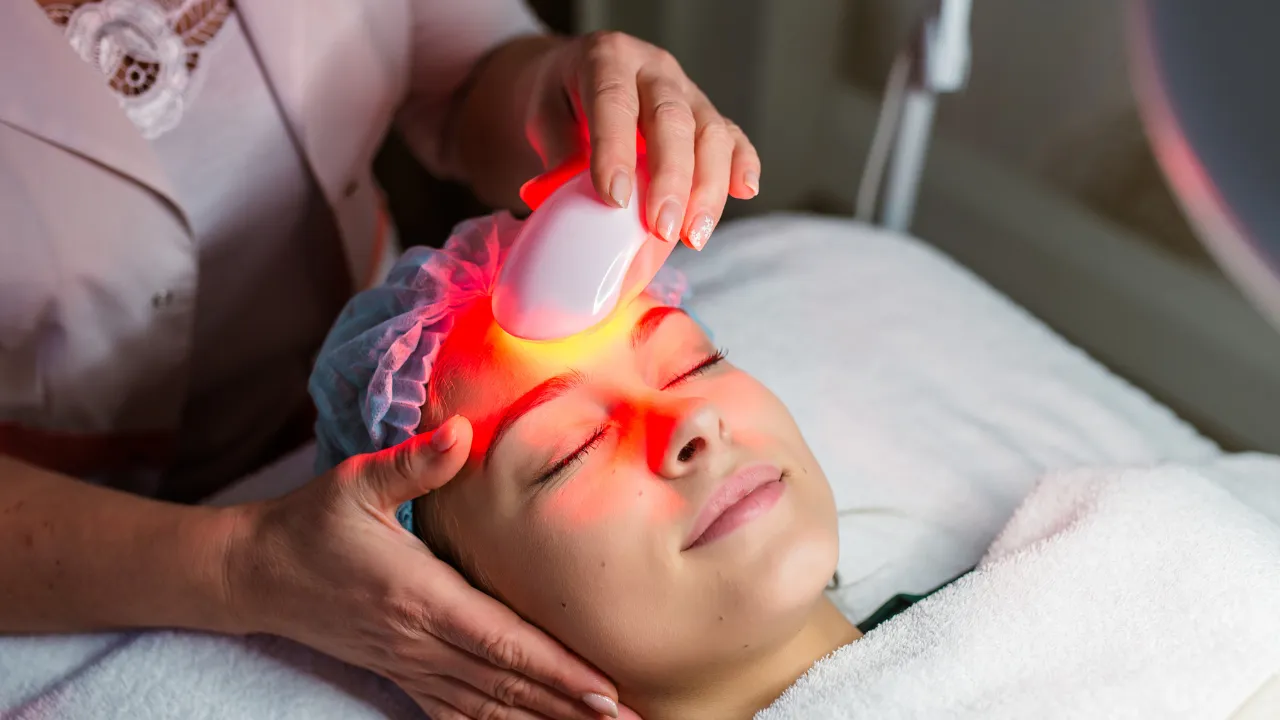
Dermal fillers for Ozempic face are used to restore facial volume lost during rapid weight loss by replacing support in areas where fat loss changes facial structure. Ozempic face develops when facial fat pads shrink faster than the skin can adapt, leading to hollowing or sagging skin rather than a surface skin issue.
This article explains how fillers address these structural changes, their limits, and key safety considerations, with clinical context from Kopelman Aesthetic Surgery and Joel Kopelman.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Takeaways
- Dermal fillers can help restore facial volume after rapid or significant weight loss, but they do not tighten sagging skin or stop aging or ongoing weight-related changes.
- Ozempic face is linked to facial fat loss during weight reduction, not to the direct effects of GLP-1 medications or other weight-loss drugs on skin or bone.
- Treatment planning depends on anatomy, weight stability, and timing, since continued weight changes can affect results and longevity.
- Safety relies on conservative use of facial fillers and a detailed understanding of facial anatomy to reduce placement-related risks.
Can Dermal Fillers Fix Ozempic Face?
Dermal fillers may help treat the Ozempic face by replacing volume lost during rapid weight reduction. The primary goal is to restore facial volume and balance rather than alter natural facial features. In clinical practice, this approach is considered a minimally invasive option when anatomy, timing, and expectations are appropriate.
Facial fillers have significant limitations. They do not tighten sagging skin, replace bone structure, or prevent future aging or continued weight loss. Understanding what dermal filler treatments can and cannot do supports informed decision-making.
What Is Ozempic Face, and Why Does It Happen?
Ozempic face describes facial hollowing that may develop after rapid or significant weight loss. Fat pads in the cheeks, temples, and midface can shrink, reducing skin support and altering facial contours. These changes often become more noticeable as facial fat loss progresses.
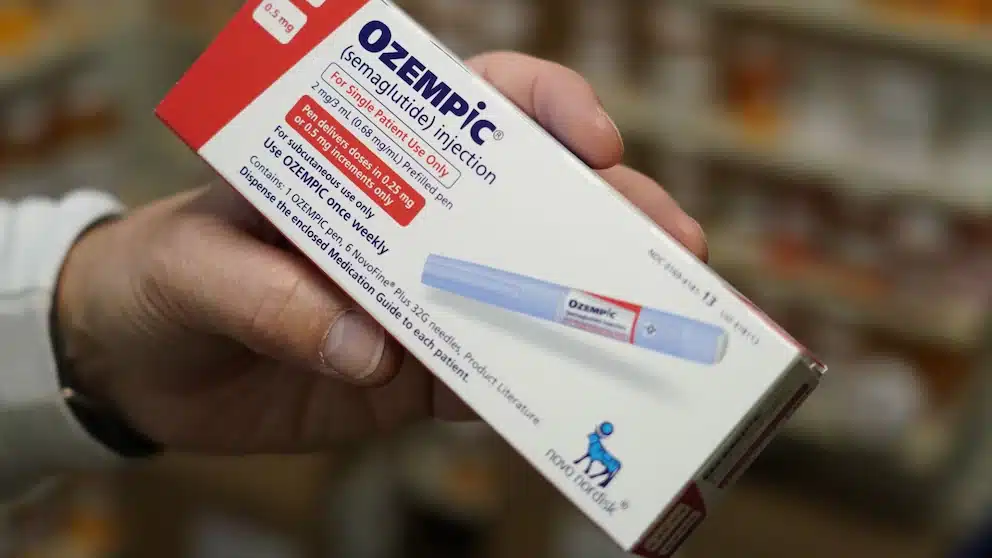
GLP-1 is a hormone in the body that helps control blood sugar and appetite. Medications like Ozempic mimic this hormone’s effects, helping people with type 2 diabetes and weight management by regulating appetite and blood sugar.
As patients lose weight, fat loss occurs throughout the body, including the face. These medications do not directly damage skin, collagen, and elastin, or bone structure.
Ozempic and Fillers: How They Work Together
GLP-1 medications and dermal fillers affect different systems in the body. One influences appetite, blood sugar control, and weight, while the other addresses facial structure. Patients may consider fillers once weight loss slows or stabilizes.
Timing plays a key role. Treating too early while weight loss is ongoing can lead to further changes that affect balance and longevity. A stable baseline supports more predictable outcomes.
Where Dermal Fillers Are Placed for Ozempic Face
Treatment focuses on areas that have lost structural support rather than on individual lines. Common placement areas include:
- Cheeks and midface to restore support
- Temples to address hollowing
- Jawline to improve contour
In many cases, midface volume loss is addressed with a mid-cheek filler approach to restore structural support and improve facial balance. Careful placement helps restore facial volume without overcorrection.
Best Dermal Fillers After Weight Loss
Hyaluronic acid–based facial fillers are often used because they integrate well with tissue and allow controlled correction. Product selection depends on anatomy and treatment goals, and understanding the best facial fillers for different facial areas helps guide appropriate planning. Anatomy, rather than a one-size approach, guides selection.
Ozempic Face With Fillers: Before and After Results
Changes from treatment are usually subtle and progressive. The goal is improved balance rather than recreating a previous appearance. In Ozempic face with fillers, patients often notice smoother contours and reduced hollowing.
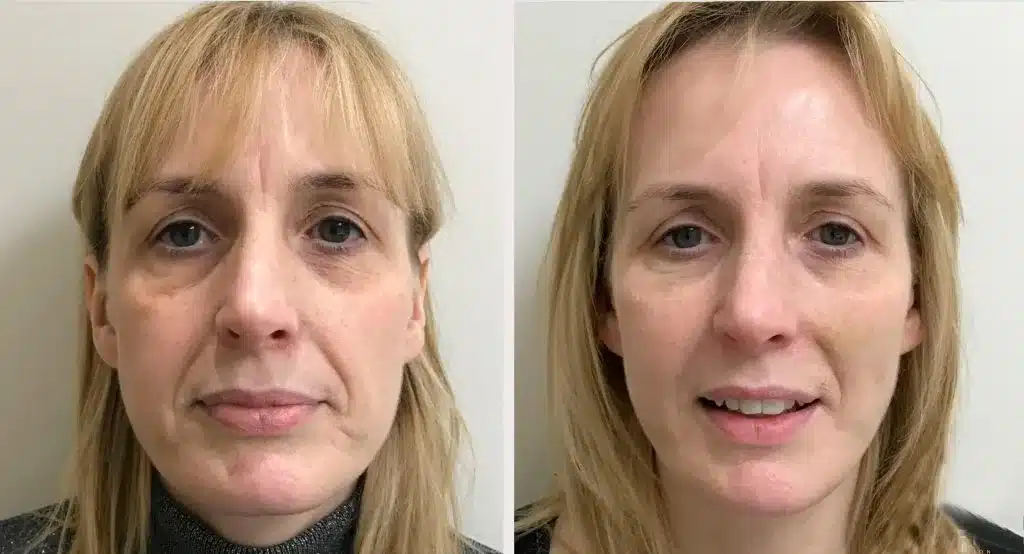
Longevity varies based on product type, placement, and metabolism. Many hyaluronic acid fillers last several months to over a year.
Side Effects and Safety of Dermal Fillers
Common side effects include temporary swelling, bruising, or tenderness at injection sites. Serious complications are uncommon when treatment follows established medical standards and anatomical principles.
Risk increases with improper placement, excess volume, or inadequate anatomical knowledge. Conservative dosing and careful assessment help reduce these risks.
Cost of Dermal Fillers for Ozempic Face
Dermal fillers for Ozempic face typically cost $700 to $1,000 per syringe, depending on the type of filler used. The total cost depends on how many syringes are needed and which areas are treated, as facial volume loss varies from person to person.
How to Fix Ozempic Face Naturally
Non-injectable approaches focus on skin quality rather than volume. Nutrition, resistance training, and skin care may support overall skin health, but do not restore facial volume lost during weight reduction.
These options are sometimes discussed alongside other treatments for the Ozempic face, but they are limited in addressing structural hollowing or sagging skin. Understanding these limits helps set realistic expectations about what natural approaches can achieve.
Treatment Process and Ideal Candidates
The treatment process begins with a clinical evaluation of facial anatomy, weight history, and the pattern of volume loss. The provider identifies areas where structural support has decreased and determines whether dermal filler treatments are appropriate based on the timing and stability of weight gain.
Treatment typically involves targeted injections to restore facial volume in specific areas, using conservative amounts to maintain balance. Sessions are usually brief, and most patients return to normal activities the same day, with follow-up visits used to assess response and make adjustments if needed.
Ideal candidates are generally healthy adults with a stable weight who notice facial volume loss after rapid or significant weight reduction. Patients with ongoing weight loss or certain medical conditions may be advised to wait before proceeding.
If you have questions about facial changes related to weight loss, you can schedule a consultation to review your options based on your anatomy and overall health.